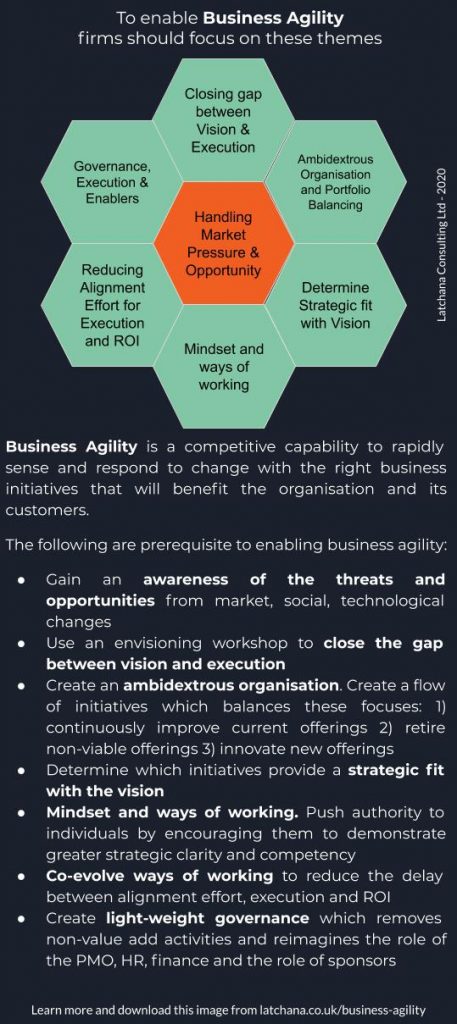
The envisioning workshop is a group facilitation activity which:
- Co-creates a shared business vision to unite behind
- Identifies and prioritises strategies which are faithful to the vision
- Generates the momentum to test and execute the strategic objectives
It helps ensure the co-created vision, strategic alignment and execution are in keeping with the elements described in Starting an Engagement.
Setup and Agenda
Participants should be the leadership team, stakeholders and key representatives from the execution team (aka delivery team). Ideally, there should be between five and nine participants, plus the workshop facilitator(s).
Duration: Typically 3-4 hours
Agenda
- Co-creation of the vision statement
- Identify measures of success
- Brainstorm strategies which will help deliver the vision
- Prioritise strategies
- Setup cadence and move into execution
Co-creation of the vision statement
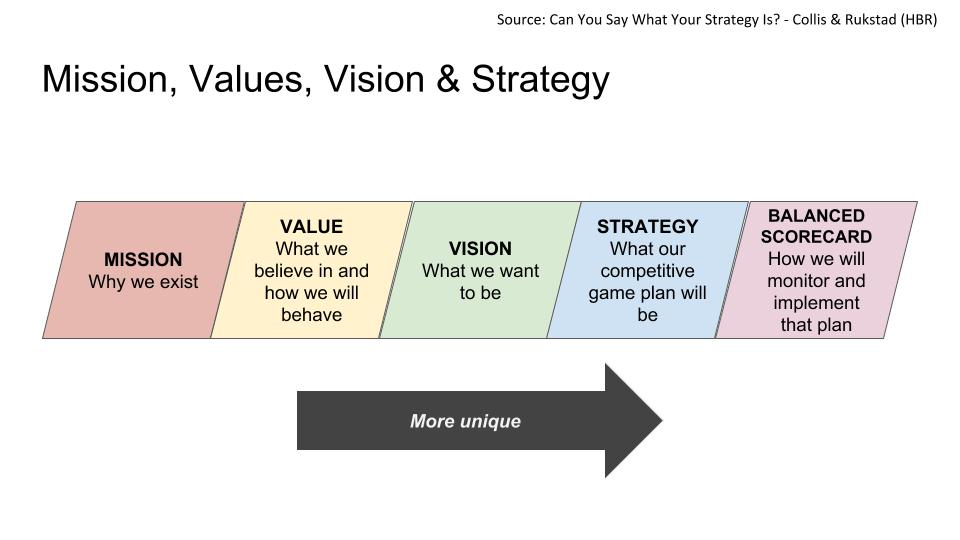
To gain alignment it’s important that all participants co-create the vision. The vision describes an ambitious and motivational future-state for the business. This vision is written as a vision statement, which has the following qualities:
- Succinct – one or two sentences
- Visionary – Drives motivation to create a beneficial future-state
- Works on the team’s behalf – Help to communicate and gain alignment across the business
- Aligns the team with their stakeholders
- Easy for everyone in the business to understand
- Scoped – removes any erroneous activities such as pet projects
To move with velocity to drive profitable growth and become an even better McDonald’s serving more customers delicious food each day around the world.
McDonald’s Vision Statement
We’ll save money by eliminating impediments to deliver a frictionless customer experience, which empowers our front-of-house colleagues.
A Vision Statement created by a team in a FTSE 100 company
Identify measures of success
Brainstorm and agree on three or four measures of success. These ensure the right benefits, behavioural changes and consequences will be achieved which will support the vision.
Some examples of measures of success:
- Reduce the cost to serve
- Increase customer retention
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Increase incremental sales
- Reduce carbon emissions across the vehicle fleet
Measures of success should be found within the vision statement. The following measures of success are implied in the McDonald’s vision statement:
- Profit growth
- Customer growth
- Customer satisfaction
- Global scope
Brainstorm strategies which will help deliver the vision
Now facilitate the participants to brainstorm a number of strategies which will meet some or all of the measures of success, which they believe will help to fulfil the vision.
If the vision is transformational, encourage the creation of strategies which will test long-held assumptions.
Participants can write their strategies individually or in pairs. Each strategy idea should be written on post-it notes. Once participants have written a few each, remove any which the participants agree are duplicates.
A strategy is something which gives consistency over time and contains the essence of how you’re going to be different
Gary Hamel’s definition of strategy
Prioritise strategies
These strategies should now be ordered relative to each other. They should be ordered by their degree of perceived value towards achieving the vision, and by the perceived complexity of achieving the strategy.
There are a number of ways to understand and measure complexity. For example, consider Liz Keogh’s Estimating Complexity and my RUDE technique.
This stage of the workshop creates a spread of strategies where the following can be identified and discussed:
- High-value strategies which are likely to have little complexity to deliver
- High-value strategies which are complex to deliver
- Low-value strategies which have little complexity to deliver
- Low-value strategies which are complex to deliver
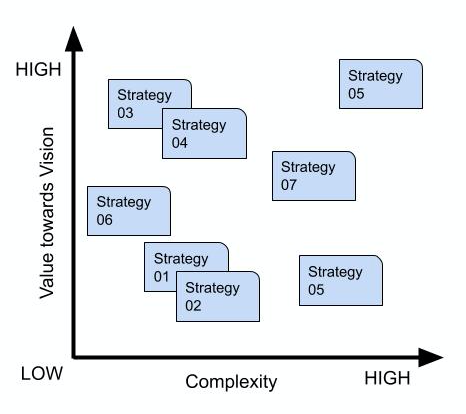
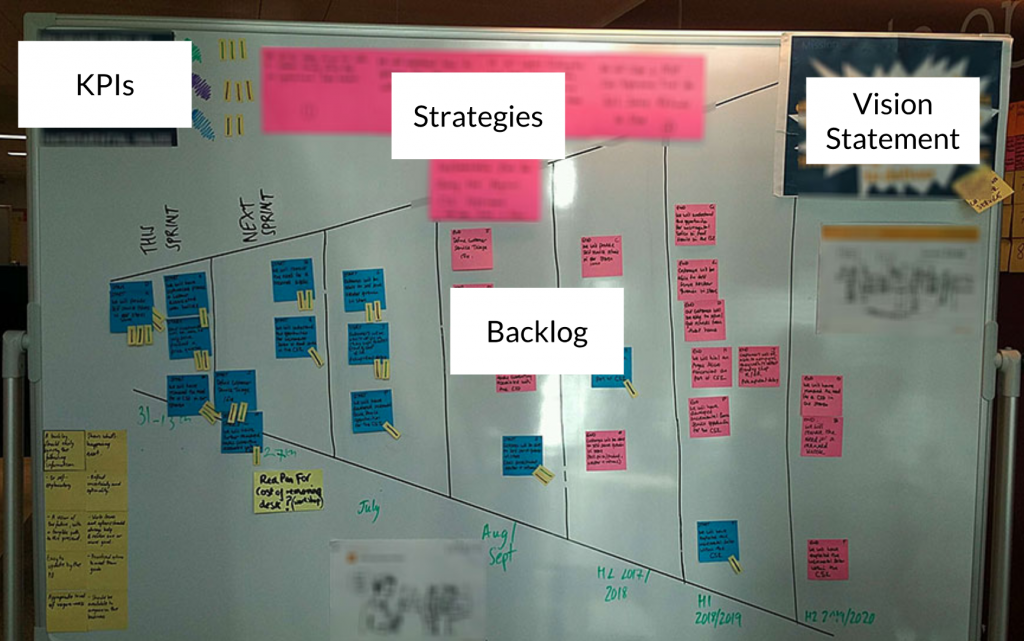
Participants should then reflect on the distribution of strategies, and be encouraged to debate, modify, reposition, and possibly remove strategies. This helps the participants create an ordered backlog of strategies.
Setup cadence and move into execution
Since each strategy has a degree of uncertainty, each strategy should be treated as a hypothesis to be proven or disproven through rapid experiments. Therefore, following the workshop, with close support of their leaders and stakeholders, execution teams should test and learn whether the strategies can be achieved.
These strategies should be tested through the innovations, products and services built by the execution teams. A Lean Startup approach should be employed utilising concepts such as the Minimum Viable Product. In partnership with the workshop participants, teams should be disciplined and ruthless in discontinuing ideas which don’t meet the strategic objectives.
A possible set of evaluation criteria can be the one described by the Ash Maurya:
- Desirability: The innovation, product or service solves a problem for the beneficiaries of the product or service
- Viability: The innovation, product or service fulfils its strategic objective
- Feasible: The innovation, product or service can be built and sustained
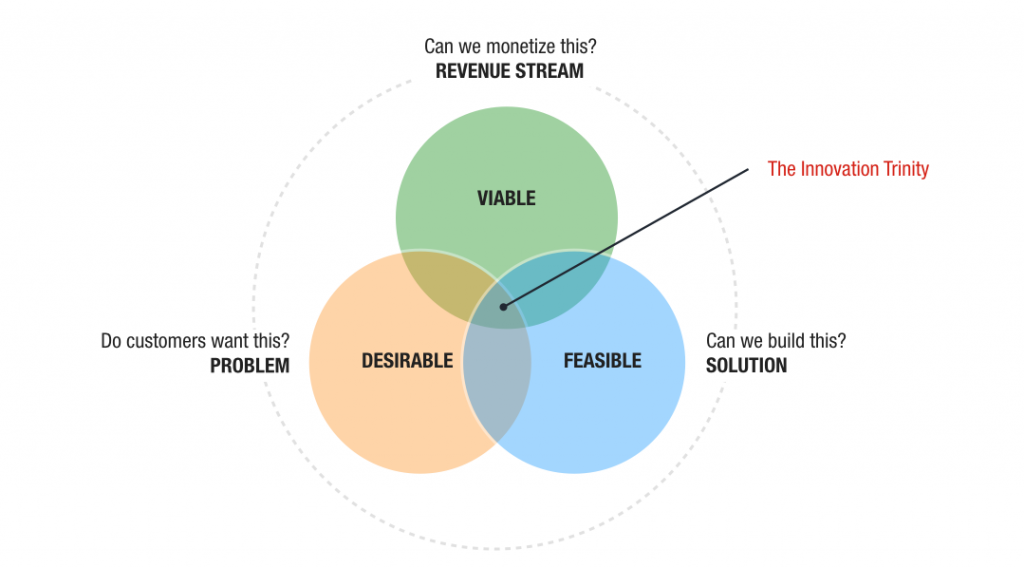
Another set of criteria could be testing for problem-solution fit and product-market fit.
A final stage of the workshop is for the participants to agree on how to brief and support execution teams to address two or three strategies from the top of the strategy backlog.
The continuation of existing strategies, innovations, products and services should be judged against their alignment to the vision and its measures of success.
A pivot is a change in strategy without a change in vision
Eric Ries
A cadence structure should be agreed and set-up for the participants to regularly meet, review and adjust the strategic fit to the vision. This should be done in union with the execution teams.
To ensure on-going alignment and support for execution teams, execution teams should be encouraged to make use of visual management techniques which demonstrates how their current and future work is testing the agreed strategies. The Cone-shaped Backlog is one such visual management technique.