Does your team tend to do the right thing, or do the thing right?
Doing the right thing means that despite any mandated procedure, sanctioned tools or external expectations, the team can choose their own approach to achieve its purpose.
Doing the thing right means that the team adheres to the mandated procedures, use the sanctioned tools and meet external expectations, even if it means it impedes them from fulfilling their purpose.
This article offers a technique that’ll enable teams to examine and potentially improve their balance of doing the right thing and doing the thing right. But first an example…
Example
Suppose a team of housing officers aren’t obligated into following ill-fitting procedures, tools, and expectations. They’ll have the freedom to find the right approach to meet their purpose to support their tenants. They will be doing the right thing. They will be discovering and evolving the right procedures, tools, and expectations to support their tenants.
If they are bound by, or hide behind the use of procedures, tools, and expectations, which aren’t fit for purpose, they will be hindered from fulfilling their purpose of supporting their tenants. They’ll be doing the thing right.
Impact of doing the thing right
Many teams feel compelled to do the thing right at the cost of doing the right thing. Lack of freedom to safely challenge, and potentially disregard, mandated ways of working can result in many suffering in silence. It often leads to poor morale, disillusionment, unmet team objectives, and delay.
In fact, the desire to be seen to do the right thing, even if the practice isn’t mandatory, can lead to unnecessary adherence.
At times the detrimental impact can lead to catastrophe, resulting in public outcry, scandal and suffering. One tragic example is the Liverpool Care Pathway scandal, where many patients in palliative care were reported in the media to have unnecessarily suffered as a result of poorly implemented guidance.
It’s reported that many patients were being assessed as terminally ill, sedated and denied water often resulting in many who might have survived longer otherwise dying prematurely.
A less harrowing, yet universal occurrence in many organisations is the expectation that teams adhere to poor-fitting frameworks and procedures. Often these are deemed by outsiders as necessary. However, these mandates were never, or are no longer, fit-for-purpose. For example an overly bureaucratic governance process, an inappropriate compliance regime mandated by distant policymakers, or an inflexible and protracted product delivery lifecycle.
Overcoming doing the thing right
How can teams overcome the pressure to do the thing right so they can focus on fulfilling their purpose? How can they recognise and challenge ill-fitting procedures, tools, and expectations?
I have a technique that will help teams map and strategise their way towards doing more of the right thing. The technique works by incrementally expanding the boundary of existing local freedoms into the area of external expectations and mandated processes.
The technique recognises that mandates may have originated from a worthy – yet possibly misconceived – desire to manage for consistency, efficiency, and alignment across the organisation.
It also recognises that since organisations need to adapt to change and uncertainty, to be effective, teams need the flexibility to safely experiment with emergent and nonconformist ways of working, which still align with the wider organisational vision.
The technique
This facilitated technique involves the team identifying the interactions, processes and tools they are involved with.
Start with identifying between six and 12 items which are routine team practices. Here are some examples:
| No. | Item | Type |
| 1 | Working with customer representative | Interaction |
| 2 | Implementing the needs of an influential Senior Manager from a different business unit | Interaction |
| 3 | Regular customer visits | Interaction |
| 4 | New governance process mandated by new parent company | Process |
| 5 | Manual document control process with no centralisation or version control | Tool |
| 6 | Web-based collaborative documentation tools. Tool introduced by the new parent company | Tool |
| 7 | Implementing unquestioned requirements based on a untested solution | Tool |
Approximately place each item onto a plot showing the value the item contributes to the team’s purpose versus the degree of control the team has to do the item.
The team could do this with post-it notes so they can be easily discussed, changed and moved around.
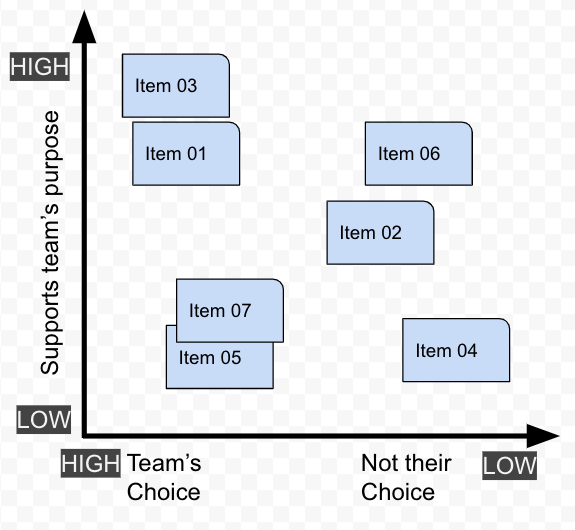
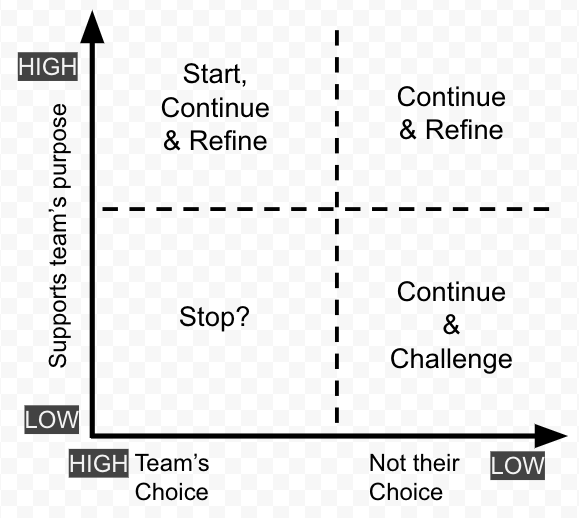
Finally, referring to the illustration below, categorise and discuss the items as follows.
| Item Mapping | Team considerations |
| Low value & team’s choice | Discuss whether the item should be stopped. This item provides little value and the team has freedom to discontinue it. |
| High value & team’s choice | This item should be continued, monitored and refined. |
| High value & no team choice | Although the item is mandated, it still provides value to the team. It should be continued and potentially refined with those mandating the item. |
| Low value & no team choice | Since it’s mandated, the team will need to continue this item. However, where possible, they should discuss with those mandating the item that it provides little value to the team’s purpose. Both parties should explore how adjustments or alternatives could address their shared needs and concerns. |
Next steps
The team should recognise this is a dynamic landscape, over which they have some agency. Therefore this technique should be done periodically, and with discipline. It will help the team continuously expand and improve upon the procedures, tools and expectations needed to fulfil their purpose.
Final thought
This technique should help the team gain a better awareness of the procedures, tools and expectations they have control over, and which they don’t. It will help move from frustration & dejection to engagement & continuous improvement.
Contact me (dean@latchana.co.uk) if you would like help introducing this technique within your organisation.